Wavelet-based stochastic finite element analysis of steel girders
1
Wydział Inżynierii Lądowej i Transportu, Instytut Analizy Konstrukcji, Zakład Mechaniki Budowli, Politechnika Poznańska, Poland
2
Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Transport, Institute of Structural Analysis, Poznan University of Technology, Poland
3
Department of Structural Mechanics, Łódź University of Technology, Faculty of Civi Engineering, Architecture and Environmental Engineering, Poland
Submission date: 2024-05-08
Acceptance date: 2024-06-03
Publication date: 2025-06-16
Corresponding author
Michał Guminiak
Wydział Inżynierii Lądowej i Transportu, Instytut Analizy Konstrukcji, Zakład Mechaniki Budowli, Politechnika Poznańska, Piotrowo 5, 60-965, Poznań, Poland
Wydział Inżynierii Lądowej i Transportu, Instytut Analizy Konstrukcji, Zakład Mechaniki Budowli, Politechnika Poznańska, Piotrowo 5, 60-965, Poznań, Poland
Archives of Civil Engineering 2025;71(2):225-242
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
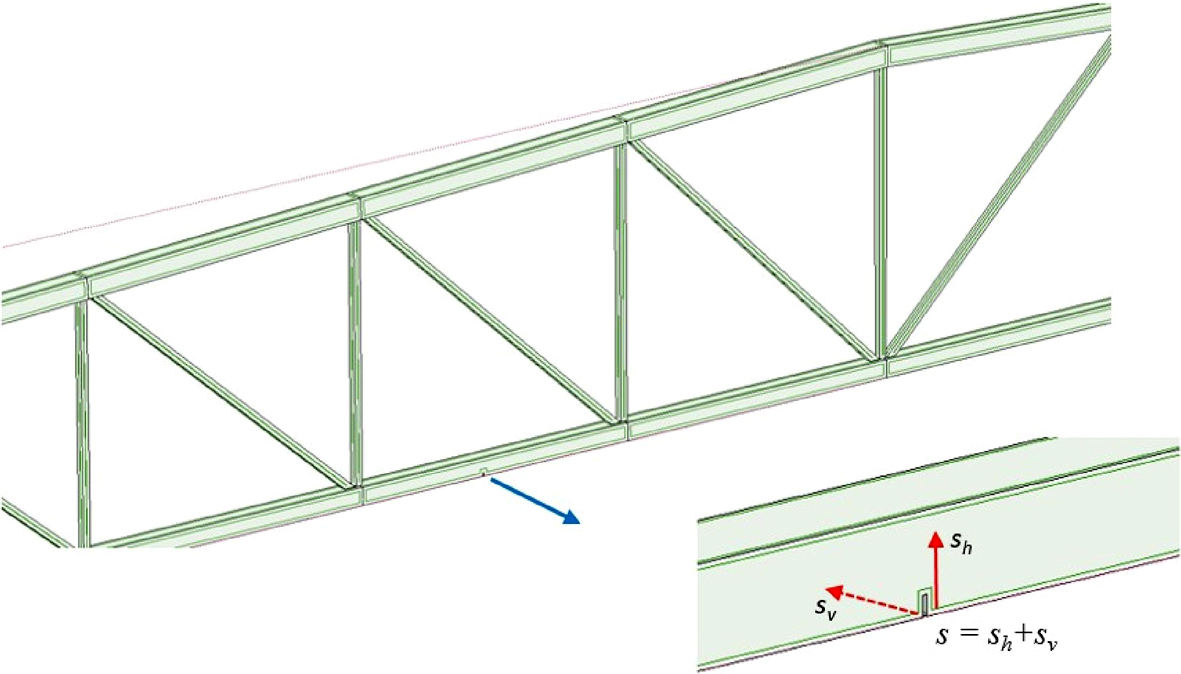
The paper presents the problem of damage detection in steel girders. Static displacements at the selected point of the structure play the role of measured variables. Structural response signal decomposition is performed according to the Mallat pyramid algorithm, which is used to perform the discrete wavelet transform (DWT). This procedure allows us to quite well determine the location of structural damage. The geometry and the placement of any defective part of the structure may have a random character. It can be assumed that the random processes occurring in the broadly understood structure mechanics are Gaussian in nature. The first four probabilistic moments are estimated using three approaches independent: semi-analytical (SAM), perturbative (SPT), and Monte-Carlo simulations (MCS). The semi-analytical random approach seems to be the most optimal due to the necessary computation time.. The incorporation of the mathematical stochastic apparatus into the classical (deterministic) analysis of the statics of the structure makes it possible to estimate the reliability measures of the analyzed girder.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.