Three-dimensional interpretation of geophysical and geotechnical investigation of landslides
1
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Warsaw University of Technology, Poland
2
Faculty of Geology, University of Warsaw, Poland
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2024-04-01
Final revision date: 2024-09-07
Acceptance date: 2024-09-17
Publication date: 2024-12-04
Corresponding author
Małgorzata Superczyńska
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Warsaw University of Technology, Armii Ludowej 16, 00-637, Warsaw, Poland
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Warsaw University of Technology, Armii Ludowej 16, 00-637, Warsaw, Poland
Archives of Civil Engineering 2024;70(4):99-111
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
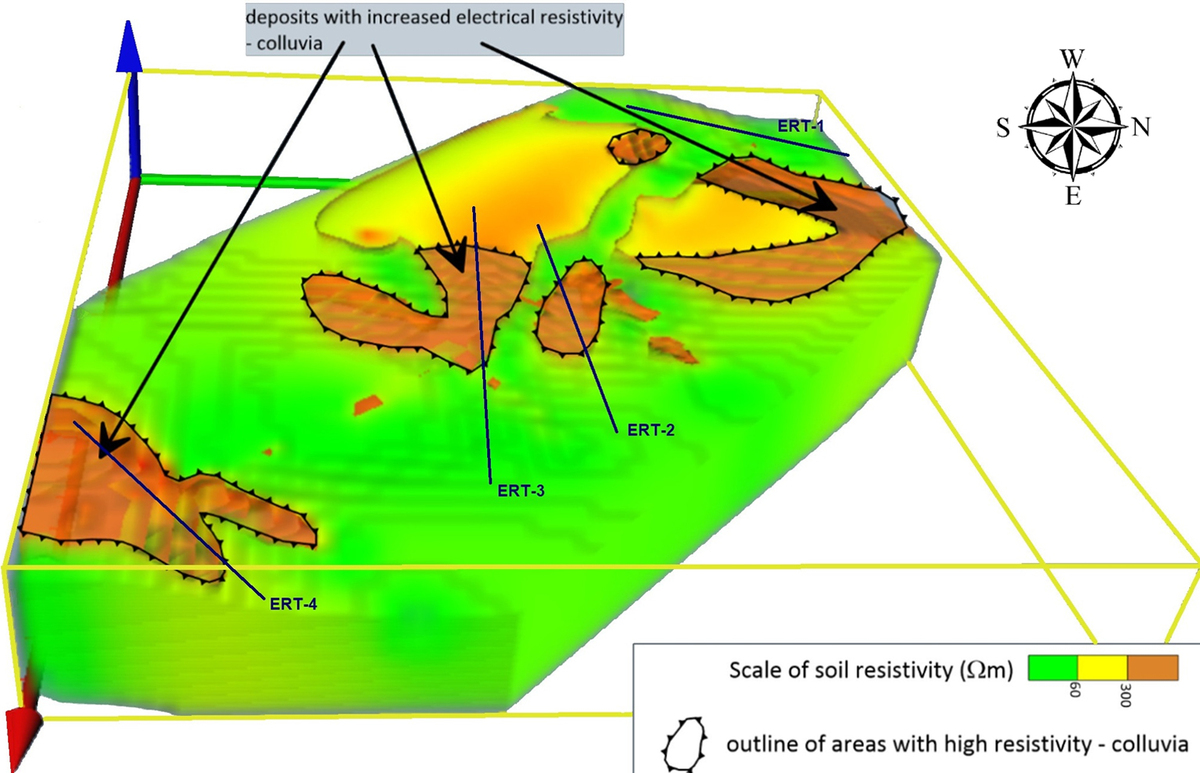
Effective engineering design of structures requires a thorough understanding of the groundwater conditions of the substrate. In some situations, a three-dimensional survey is necessary. Landslides are examples of such cases. They are complex phenomena, and the main factors significantly influencing their behaviour over time are changes in slope geometry, inclination and water conditions. The article discusses the reconnaissance of the substrate structure in an area threatened by mass movements along a modernized section of a railway line. The analysed area is located in the marginal zone of the North Polish glacial moraine. The geological structure of the substrate consists of: glacial tills, glaciofluvial sands, lacustrine clays, and organic soils found in periodically waterlogged areas and depressions in the terrain. Colluvial deposits, mainly consisting of clayey formations, occur on the slope of the escarpment. Surface geomorphology was interpreted using LIDAR data and field observations. Two-dimensional and three-dimensional electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) was used to obtain a detailed subsurface image, which was verified by borehole drilling and laboratory analysis of soil samples for physical properties, including grain size distribution and plasticity, as well as mechanical properties of soils. This research enabled the creation of a three-dimensional substrate model, showing the spatial distribution of colluvium and areas at risk of active landslides. The results indicate that an integrated approach, combining geophysical imaging and geotechnical reconnaissance, allows for a detailed understanding of the structure and lithology of landslide areas.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.