The use of bottom and a mixture of bottom and fly ash from wood-sunflower biomass combustion in concrete production
1
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Czestochowa University of Technology, Poland
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2024-01-18
Final revision date: 2024-03-13
Acceptance date: 2024-04-16
Publication date: 2025-06-16
Corresponding author
Jakub Jura
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Czestochowa University of Technology, Dąbrowskiego 69, 42-201, Częstochowa, Poland
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Czestochowa University of Technology, Dąbrowskiego 69, 42-201, Częstochowa, Poland
Archives of Civil Engineering 2025;71(2):19-35
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
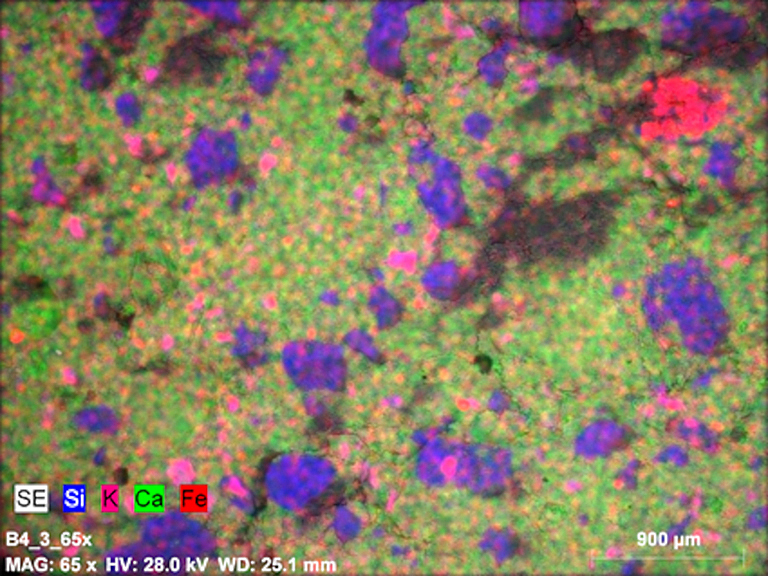
As part of the research, concrete mixes containing the addition of bottom ash as well as bottom and fly ash mixtures from the combustion of biomass only were made. The ashes were obtained from the combustion of 80% of wood and 20% of sunflower in a fluidized bed boiler. In the study, the elemental composition of ashes was determined by testing with an XRF X-ray spectrometer. Ashes in the amount of 10, 20 and 30% of the cement mass were used as a substitute for sand for testing concrete samples. During the preparation of concrete mixes, tests of consistency and air content in the mixes were carried out. Concrete samples were tested in terms of e.g. compressive strength, water absorption or frost resistance. The compressive strength of the samples with the addition of bottom ash was lower than the strength of the control samples. The use of a mixture of ashes allowed to improve this property and each of the samples obtained a higher compressive strength than samples without the addition of ash. The addition of ashes significantly improves the frost resistance of concrete, i.e. reduces the decrease in the compressive strength of concrete after frost resistance tests. The absorbability of the samples, regardless of the amount and type of added ash, changed slightly in relation to the control samples.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.