The optimization model of building construction based on BIM and improved NSGA-III algorithm
1
Construction Management, Chongqing Metropolitan College of Science and Technology, China
Submission date: 2024-01-17
Final revision date: 2024-05-08
Acceptance date: 2024-05-28
Publication date: 2025-06-16
Corresponding author
Archives of Civil Engineering 2025;71(2):5-18
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction
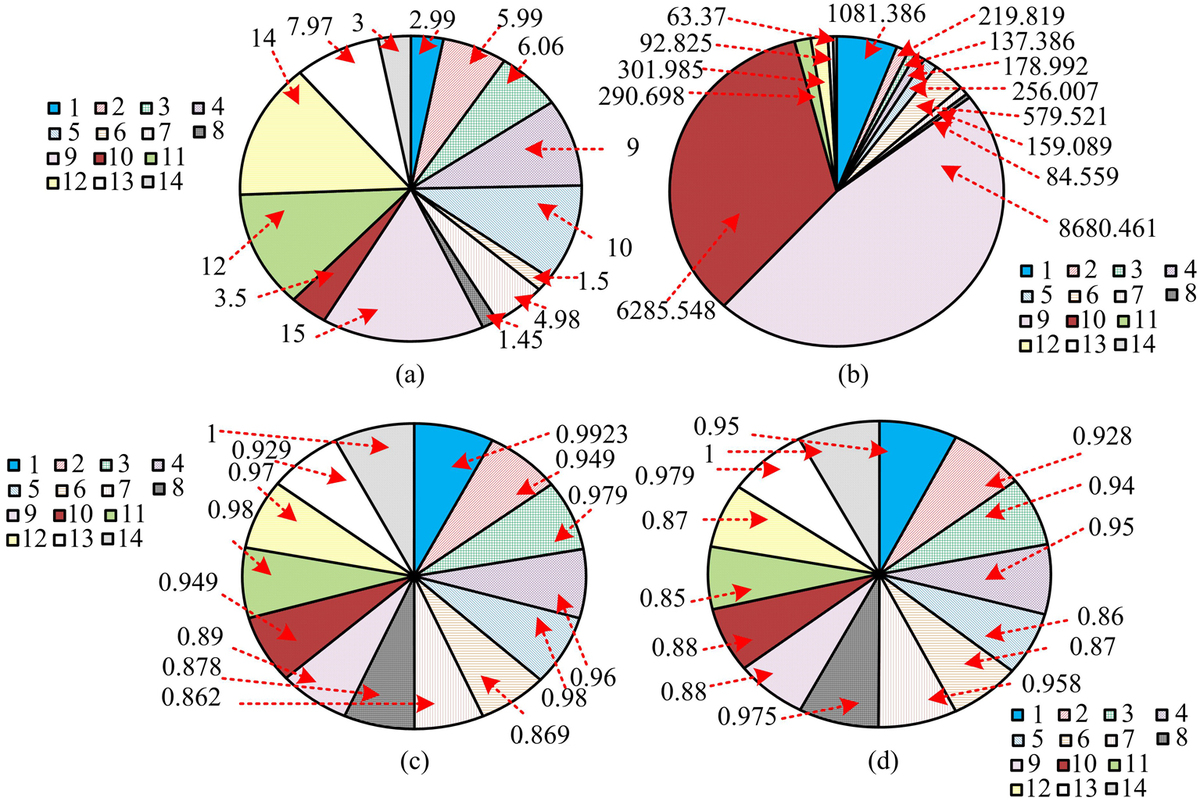
Currently, there are difficulties in dealing with higher construction requirements and standards in subway construction management. Therefore, a multi-objective optimization model was constructed based on building information management technology, and an improved non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm III was introduced to optimize the model solution. And experimental verification was conducted. These experiments confirmed that the average HV of the improved algorithm was 0.67, which was higher than the original algorithm's 0.65, indicating that it had higher convergence and reliability. The solution results of the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II showed that the optimized cost was 185.1899 million yuan. The cost of optimizing the original non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm III was 184.6469 million yuan. The total cost of optimizing the research algorithm was 184.1165 million yuan. In addition, the research algorithm had the shortest construction period, ideal cost, and significantly higher quality and safety levels than the comparison algorithms. And its time consumption was only 20 seconds, significantly lower than the comparison algorithms. And its cost was between 183 million to 187.5 million yuan, with higher stability and relatively concentrated distribution of solutions. Overall, the subway construction optimization model based on building information management and non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm III has high effectiveness and can be effectively applied in practical construction management.
Material and Methods
Results
Conclusions
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.