Optimisation of decision making for construction projects of assembly buildings based on improved PSO algorithm
1
Faculty of Engineering and Economics, Henan Finance University, China
Submission date: 2024-01-30
Final revision date: 2024-04-19
Acceptance date: 2024-05-14
Publication date: 2025-03-20
Corresponding author
Archives of Civil Engineering 2025;71(1):113-125
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
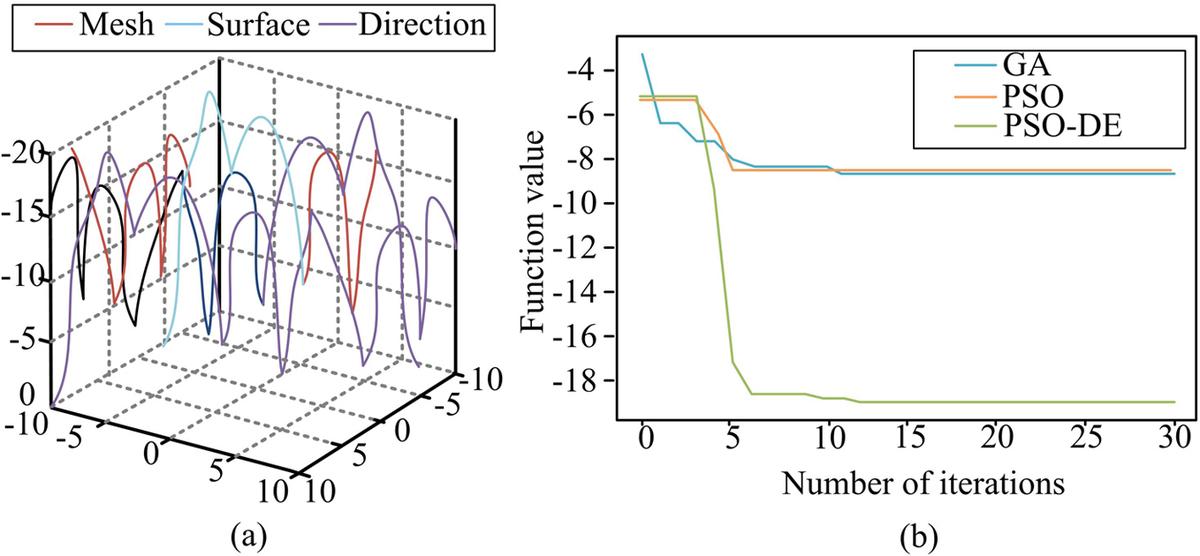
A cutting-edge construction method called fitted construction allows for several parallel lines of work to speed up construction and enhance building quality. However, achieving optimal project decisions for global construction projects demands a high level of objective decision-making. To enhance the decision-making process, this research utilizes particle swarm algorithms to optimize construction project decisions in assembled buildings. To tackle the issue of early convergence in particle swarm algorithms, three swarm enhanced particle swarm algorithms are proposed by merging the variational mechanism of the differential evolution algorithm and quantifying the decision making tasks for assembly building construction projects to be solved by the enhanced particle swarm algorithm. Regarding the research results, the upgraded particle swarm algorithm achieved a fundamental convergence in 20 iterations whilst resolving the Sphere, Rosebrock, Rastrigin, and Griewank functions. The improved particle swarm algorithm converges to an optimal solution of -19.208 within 20 iterations on the Holder function, with an optimal domain of [8.055, -9.665]. The results of the optimization study for the decision-making problem of the assembly building project demonstrate that implementing Sigmoid smoothing yields a minimum duration problem of 0.755 and a minimum duration of 45 days. The optimal cost and time required to solve the problem of economic maximisation strategy using the enhanced particle swarm method are 500,000 and 52 days, respectively. The results indicate that the improved particle swarm approach outperforms conventional algorithms in the decision-making process for assembly building projects, maintaining computational accuracy throughout.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.