Efficiency multi-agent model assisted Moea/D algorithm for optimization design for building taking into account annual energy consumption and annual user discomfort hours
1
Mechanical and Engineering, Wuhan University of Engineering Science, China
2
None, CITIC General Institute of Architectural Design and Research Co., Ltd, China
Submission date: 2023-12-01
Final revision date: 2024-02-01
Acceptance date: 2024-02-20
Publication date: 2024-12-10
Corresponding author
Archives of Civil Engineering 2024;70(4):477-489
KEYWORDS
energy efficiencymulti-agent modelmulti-objective optimization evolutionary algorithm based on decompositionannual energy consumptionannual user discomfort hours
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
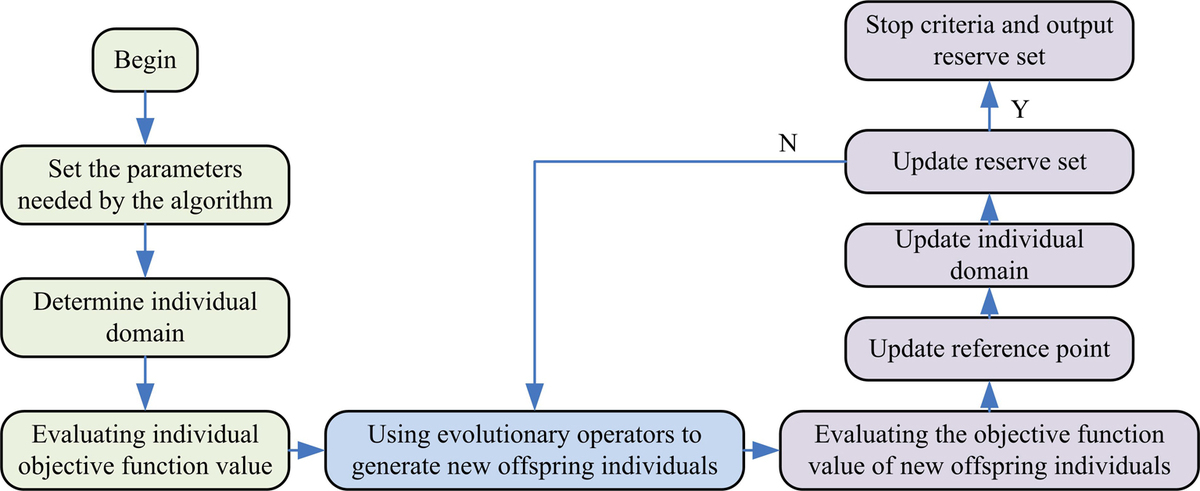
Recently, with the continuous consumption of energy, building energy conservation has been popular in the energy field. In response to the high computational cost, slow convergence speed, and low accuracy of existing optimization design methods for building energy efficiency, this study first built a multi-objective optimization model for building energy efficiency on the ground of the annual energy consumption of buildings and the quantity of uncomfortable hours for users. Then it introduces a multi-agent model auxiliary mechanism to improve the decomposition based multi-objective evolutionary optimization algorithm, and then solves the multi-objective optimization model for building energy efficiency. In order to select the optimal decision variable of the algorithm, the decision parameters were analyzed and found that the performance was optimal when the number of samples, aggregation number and base model were set to 25,3 and 20. The improved multi-objective evolutionary optimization algorithm on the ground of decomposition has average supervolume and running time values of 32416.13 and 1774.58 seconds under office buildings, and 7899.13 and 3616.96 seconds under residential buildings, respectively. In addition, the annual user discomfort time of office buildings is 555.28h, which is lower than other comparison algorithms. In summary, the optimal performance of the algorithm when the decision variable is set to 25,3 and 20. The algorithm proposed by the research institute has superior performance and has certain application value in selecting the optimal solution for building energy-saving design.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.