Punching shear of RC slabs exposed to fire: assessment of load-bearing capacity based on European and American provisions. Part 1 – General code requirements.
1
Institute of Building Engineering, Department of Concrete and Metal Structures, Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Poland
2
Department of Structural Engineering, Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Poland
3
Department for Building Technology, Linnaeus University, Sweden
4
Civil Engineering Faculty. RC and PC Structures Department, Cracow University of Technology, Poland
Submission date: 2025-01-26
Final revision date: 2025-07-01
Acceptance date: 2025-08-26
Publication date: 2025-12-01
Corresponding author
Paweł Chudzik
Institute of Building Engineering, Department of Concrete and Metal Structures, Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering, 16 Armii Ludowej Avenue, 00-637, Warsaw, Poland
Institute of Building Engineering, Department of Concrete and Metal Structures, Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering, 16 Armii Ludowej Avenue, 00-637, Warsaw, Poland
Archives of Civil Engineering 2025;71(4):31-42
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
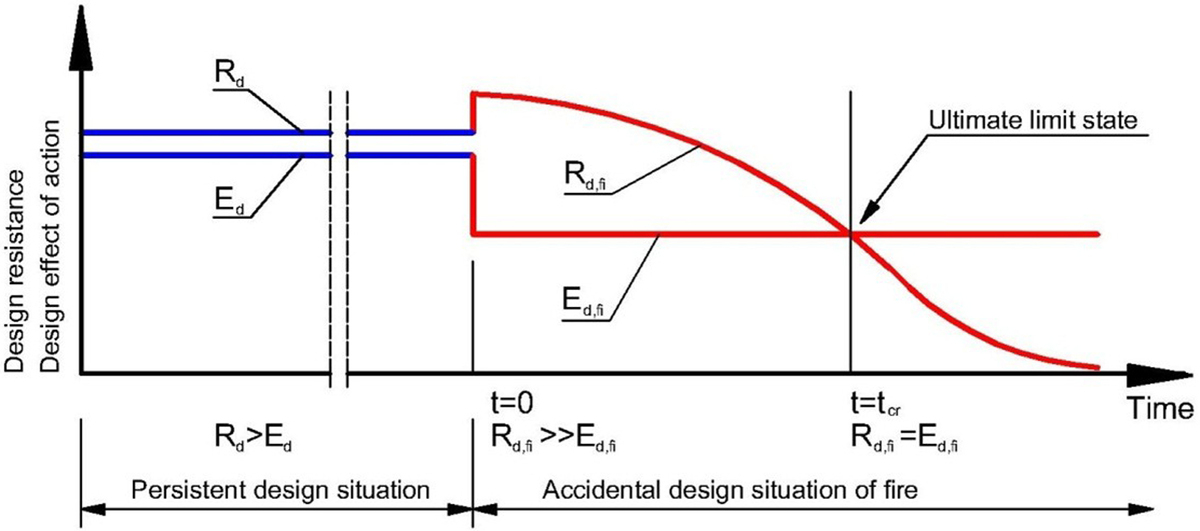
Abstract: Slab-column connection is one of the most critical points in reinforced concrete structures. Punching shear capacity of this connection must be properly determined in both the persistent design situation and the accidental design situation of fire. European and American codes give simplified (tabulated) requirements for minimal slab thickness and minimal column cross-section width in accordance with the required fire resistance. In many cases more accurate prediction of fire resistance might be needed. It can be achieved when the ultimate limit states of a structure are checked in the case of fire conditions. This paper shows the comparison between European and American code requirements for punching shear capacity as the base for further calculations of flat RC slabs subjected to fire. The second part is going to present European and American requirements for determining the effects of loads relevant to the consideration of an accidental design situation of fire and comparing these effects with the punching shear capacity of the slab-column connection, which decreases with fire duration.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.