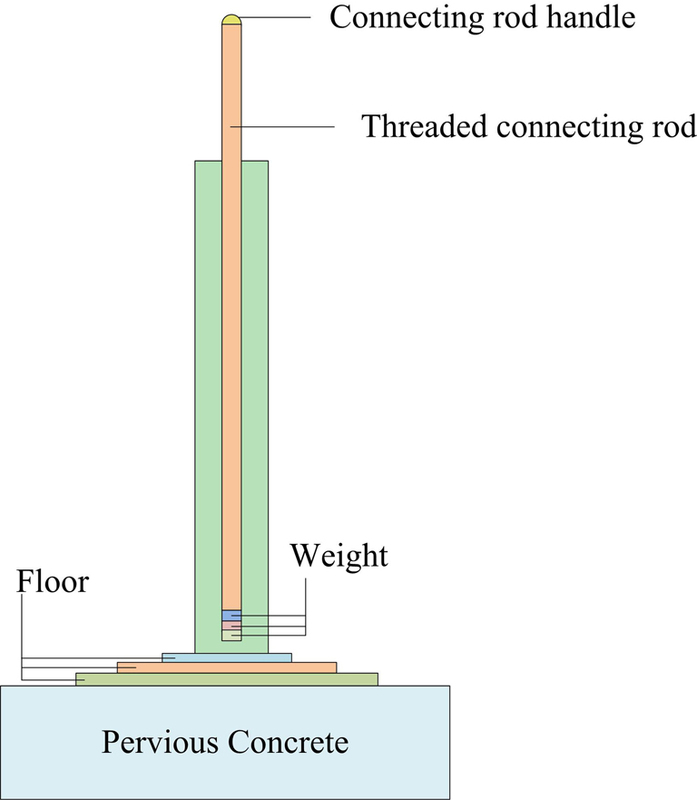
Preparation and performance of steel slag and recycled brick aggregate modified concrete under the background of solid waste application
1
Resources Environment and Architectural Engineering, Chifeng University, China
Submission date: 2023-11-03
Final revision date: 2023-12-29
Acceptance date: 2024-01-23
Publication date: 2024-10-01
Corresponding author
Archives of Civil Engineering 2024;70(3):373-386
KEYWORDS
Mechanical propertiesSteel slagSolid waste resourcesRecycled brick aggregatePermeable concreteFrost resistance
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Permeable concrete has the characteristics of breathability, permeability, and high heat dissipation. To improve its mechanical and frost resistance properties, this study optimized the preparation and performance of permeable concrete by adding materials to improve its performance. The performance analysis validate that epoxy resin owns a filling effect on the pores of permeable concrete. The internal curing agent, high water absorbent resin, has a good water absorption effect. The synergistic effect of these two increases the density and compressive strength of permeable concrete. When the two contents are 0.5%, the maximum compressive strength of modified permeable concrete at 7 and 28 days was 15.62 and 17.97 Mpa, respectively. Under the action of freeze-thaw cycles, its mass loss rate show an upward trend By comparison, epoxy resin and high water absorbent resin are beneficial for improving the frost resistance of permeable concrete. The minimum value of relative dynamic modulus of elasticity remains stable at over 80%, and the loss rate of dynamic modulus of elasticity is all below 0.4. However, the influence of epoxy resin and SAP on the mass loss rate is relatively small, and the mass loss of all experimental groups is controlled below 2.5%. The binomial Fourier function model is the best predictive model for permeable concrete under freeze-thaw cycles. This study has positive significance for improving the performance of permeable concrete and maintaining the sustainable development of ecological cities.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.