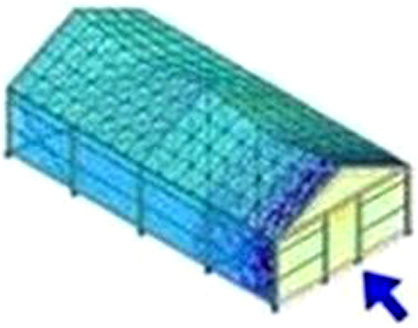
Parametric shaping of steel hall structures with modular curved roofs – preliminary comparative analysis
1
Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Architecture, Rzeszow University of Technology, Poland
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2025-05-28
Acceptance date: 2025-06-17
Publication date: 2025-12-01
Corresponding author
Patrycja Lechwar
Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Architecture, Rzeszow University of Technology, Poland
Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Architecture, Rzeszow University of Technology, Poland
Archives of Civil Engineering 2025;71(4):185-199
KEYWORDS
bar structuresgenetic algorithmshyperbolic paraboloidmodular structuresparametric shapingsteel halls
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Structures of halls with curved roofs are gaining popularity in modern industrial architecture due
to their unique aesthetic and functional advantages. This study presents a comparative analysis of the
efficiency of steel hall structures featuring frame systems and curved roofs composed of hyperbolic
paraboloid (HP) modules. Utilizing Rhinoceros 3D software along with its generative modeling and
structural analysis plug-ins, a script was developed to parametrically define the structural models and
preliminarily determine geometries within a specified range of variable parameters. These parameters
included column heights, total frame heights, frame widths, frame spacing, and the spacing of the roof bar
grid. Parametric modeling enabled the generation of numerous variants of single-nave hall structures with
five frame systems. All halls were designed with a rectangular plan measuring 12 x 24 meters and a
maximum height of 8 meters. Subsequently, structural analysis was conducted using Autodesk Robot
Structural Analysis Professional software, focusing on optimization in terms of mass and dimensioning.
The analysis considered the feasibility of using sheet metal roofing as well as flat panels, which required
adjustments of the roof bar grid topology. Variants were selected based on their efficiency and functionality.
The procedure for shaping steel halls with curved roofs using genetic algorithms proved to be highly
beneficial in the design process. The results of the analysis provide valuable guidelines for designing halls
with HP module roofs.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.