Measurement and modelling of the temperature distribution caused by the heat of cement hydration
1
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Wrocław University of Science and Technology, Poland
Submission date: 2023-08-06
Acceptance date: 2023-09-12
Publication date: 2024-09-29
Corresponding author
Andrzej Helowicz
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Wrocław University of Science and Technology, Na Grobli 15, 50-421, Wrocław, Poland
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Wrocław University of Science and Technology, Na Grobli 15, 50-421, Wrocław, Poland
Archives of Civil Engineering 2024;70(3):225-239
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
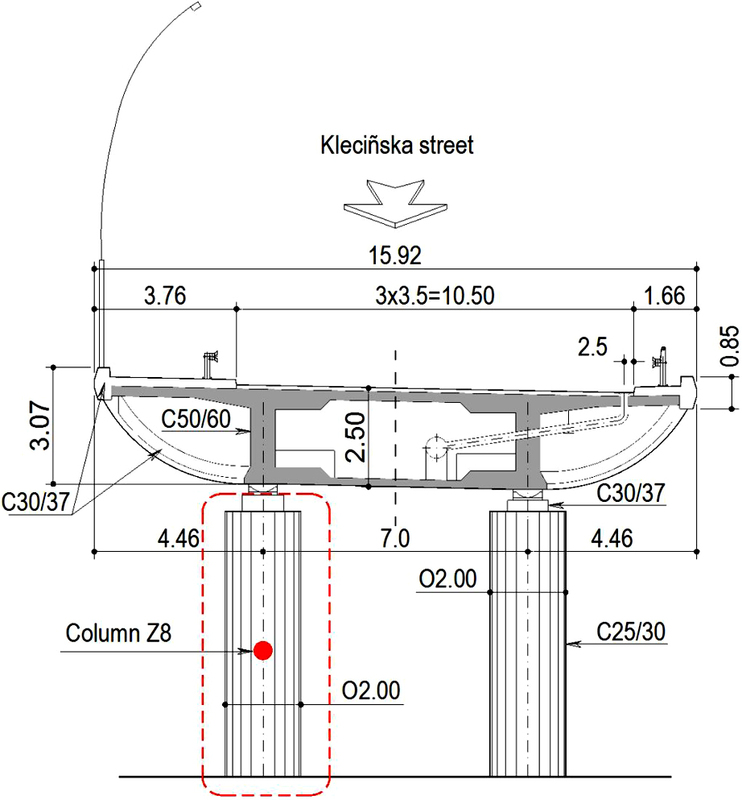
This paper describes the author's method for the direct and continuous measurement of the temperature distribution during the initial period of hardening concrete, together with the results of tests obtained with its use. The first successful test using this method was conducted by the author in May 2001 [7]. In the following years, the author successfully used this method in the study of other structural elements [8-12]. He independently developed and made the necessary elements to measure the temperature in hardening concrete. The tested element is a reinforced concrete column with a diameter of 2.0 m and a height of 8.0 m, which is an intermediate support for the flyover under construction along the Wrocław city ring road. The structure consists of two independent continuous 15-span structures made of pre-stressed concrete (see Figure 1). The article additionally presents numerical model of the previously tested reinforced concrete pillar and the calculation results obtained. The numerical calculations were carried out using the Abaqus FEA software [1]. In conclusions, the author summarises the important elements of the on-site test and makes recommendations for further use of this method to predict the temperature distribution in other elements of the structure, provided that they are made of exactly the same concrete mixture.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.