Form-finding of optimal cable nets under self-weight based on the Force Density Method
1
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Warsaw University of Technology, Poland
Submission date: 2023-08-04
Final revision date: 2023-10-04
Acceptance date: 2023-10-31
Publication date: 2024-09-29
Corresponding author
Archives of Civil Engineering 2024;70(3):241-256
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
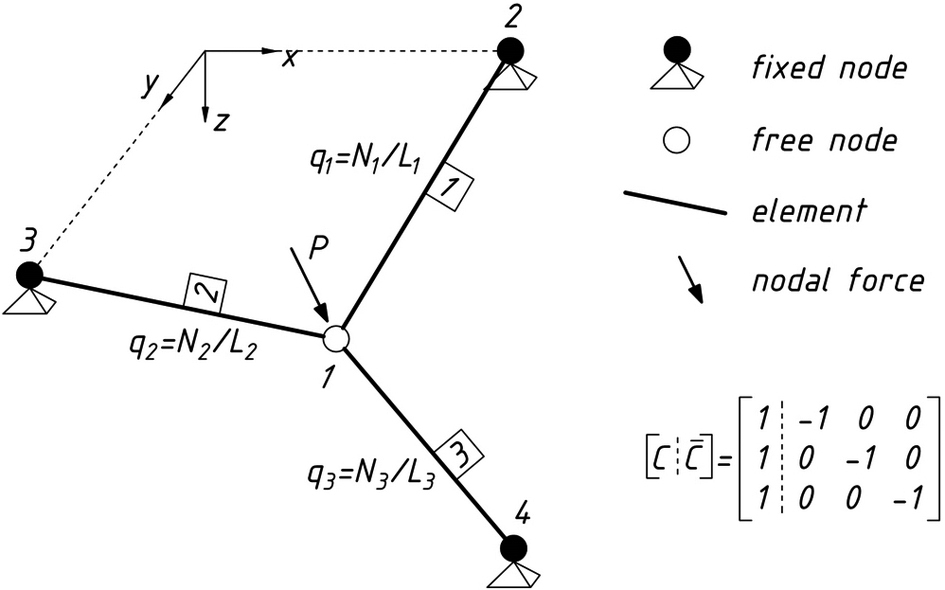
Form-finding of cable nets is the main topic of this paper. This initial stage of design path is grounded on the enhanced version of the Force Density Method. Apart from the basic form-finding it includes optimal shaping and adding self-weight of a cable structure. Minimal sum of cable lengths in the structure is treated here as a favourable initial configuration for reaching geometry and force distribution under prestress and self-weight. Regarding tensile forces obtained this way, cable sections can be proposed as the first approximation in further design process not included in this analysis. The basics of classic version of the Force Density Method are introduced in the paper. The nonlinear version of this method is used to solve an optimization problem of minimum weight cable net. The essentials of the procedures for achieving optimal shape and adding self-weight are also included and constitute the Extended Force Density Method proposed by the author. Defining proper input data for the self-weight analysis is crucial to find a new shape possibly close to the optimal one and is also discussed. A few examples of optimal or partially optimal cable nets are presented. It is shown that adding self-weight and elastic material properties can preserve the optimal shape with high accuracy. This allows to switch from the purely geometric problem of form-finding to the initial form of a structure with assumed sections and material. All calculations are performed with the use of the self-developed program UC-Form which is also briefly presented.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.