Damage characteristics analysis of self-anchored suspension bridge
1
Key Laboratory of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration, China
2
Engineering Department, Ningbo Traffic Engineering Construction Group Co., LTD, China
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2024-05-25
Final revision date: 2024-07-12
Acceptance date: 2024-11-05
Publication date: 2025-12-01
Corresponding author
Xilong Zheng
Key Laboratory of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration, China
Key Laboratory of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration, China
Archives of Civil Engineering 2025;71(4):283-298
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
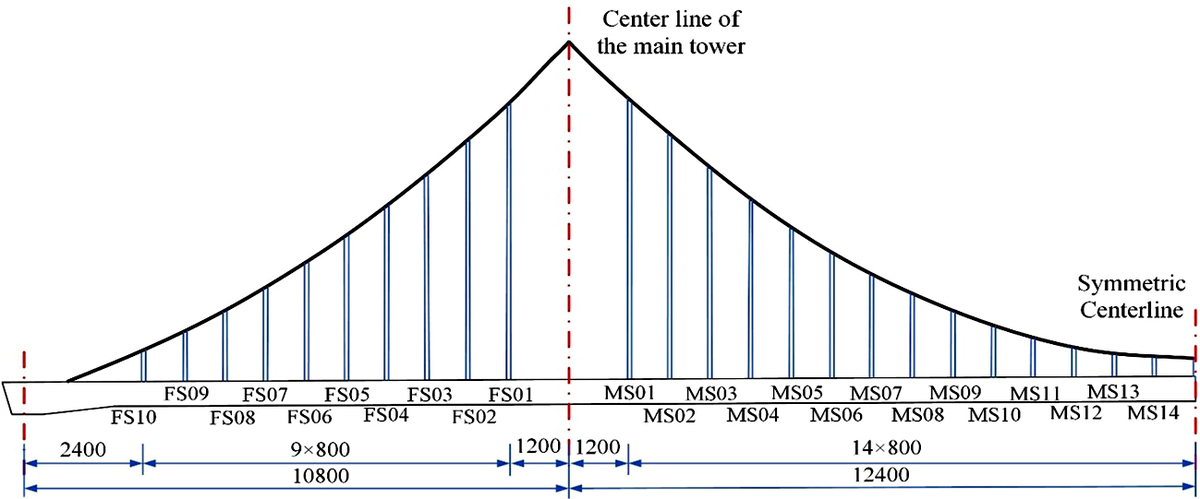
Based on a self-anchored suspension bridge with a long span and complex structure, this paper makes a detailed analysis of its stress characteristics before damage and damage characteristics after damage through finite element analysis and bridge load test. Aiming at the main vulnerable components of the main girder, a variety of identification methods based on the existing dynamic damage identification methods are selected for comparative analysis of damage identification, and finally an effective method suitable for bridge girder damage monitoring is determined according to the identification effect of each method. Different damages of main girder, bridge tower and suspender are simulated respectively, and then the static and dynamic damage characteristics of the structure under the same conditions before and after the damage are analyzed with the results of nondestructive analysis of the bridge as reference. The results show that the internal force and deformation caused by the same static and dynamic load and the inherent dynamic characteristics of the structure will change correspondingly when different damages occur to the structure, but the change is small for the moderate damage of 20%. After the suspenders fail completely, the deformation and internal force of the bridge will increase greatly, and the cable force of the adjacent suspenders will increase by 50%.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.