Analysis of damage identification of self-anchor suspension bridge
1
School of Intelligent and Architectural Engineering, Harbin University, China
2
Key Laboratory of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, Institute of Engineering Mechanics,China Earthquake Administration, China
3
School of Civil and Architectural Engineering, Harbin University, China
4
General Affairs Department, Liaoning Trading Maintenance Engineering Co., LTD, China
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2024-05-29
Final revision date: 2024-07-17
Acceptance date: 2024-07-30
Publication date: 2025-09-16
Corresponding author
Archives of Civil Engineering 2025;71(3):385-398
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
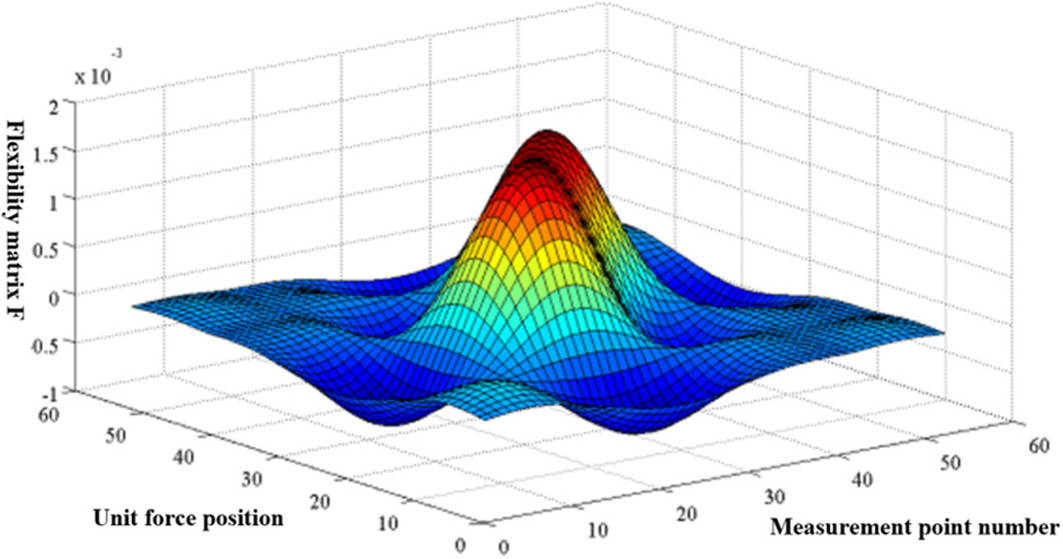
For the self-anchored suspension bridge with long span and complex structure, based on the finite element analysis, combined with the bridge load test, this paper makes a detailed analysis of its stress characteristics before damage and damage characteristics after damage, and on this basis, for the main vulnerable components of the main girder, selects a variety of identification methods based on the existing dynamic damage identification methods for comparative analysis, and finally determines an effective method suitable for bridge girder damage monitoring according to the identification effect of each method. For the main girder of vulnerable components of self-anchored suspension bridge, according to the mechanical characteristics of each section and the position relationship with the assumed dynamic sensors, five damaged beam segments are set, and each damage is given three levels of damage of 10%, 20% and 40% respectively. Then, based on the damage judgment effect of single damage and combined damage to these five beam segments, the indexes suitable for main girder damage identification are found out from various existing damage identification indexes used. Finally, CMSE is selected as the main method for damage monitoring of main girder of self-anchored suspension bridge because of its full damage identification ability and good noise resistance.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.