Soft soil foundation treatment of hydraulic fill site based on vibration boosting drainage consolidation method
1
Mining Engineering, Shanxi Institute of Energy, China
Submission date: 2023-11-14
Final revision date: 2024-01-15
Acceptance date: 2024-01-23
Publication date: 2024-10-01
Archives of Civil Engineering 2024;70(3):431-444
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
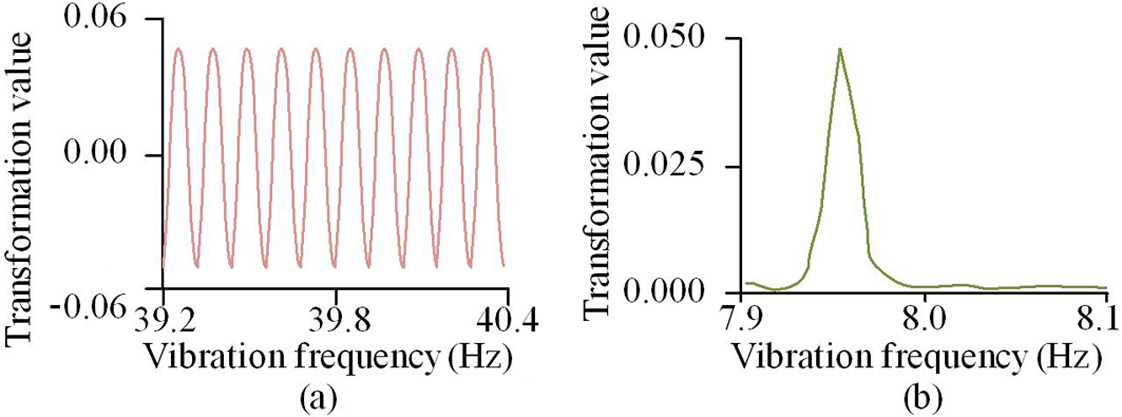
Reclamation from the sea is a method of expanding urban area, but it also faces the problem of difficult treatment of soft soil foundation by hydraulic reclamation. Therefore, a soft soil consolidation method that combines vibration pressure boosting drainage and piled-load static pressure stacking is now proposed. To verify the effectiveness of this method, a consolidation test based on soft soil samples was designed and conducted in the study. The test results showed that when the sampling height was 240mm, the overall moisture content of the consolidated soil sample was the highest, 44.3%, and the consolidation effect was the worst. When the sampling height was 140mm, the overall moisture content obtained from the test was the lowest, 43.1%, and the consolidation effect was the best. The displacement of corner 2 and center point at the intersection of the preceding and following periods was greater, with values of 37.1mm and 39.2mm, respectively. At this point, the displacement of corner 1 was significantly smaller, at 30.9mm. In the later loading stage, the slope of the vertical displacement curve significantly increased. When the experimental time reached 7000min, the mixed method designed in this study had a drainage rate of 0.53ml/min, which was significantly higher than other traditional methods. The experiment outcomes indicated that the method designed in this study had certain application potential for improving the consolidation effect of soft soil foundation in hydraulic fill sites.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.