Digital landscape architecture design using high resolution remote sensing image interpretation
1
College of Architectural Art Design, Luxun Academy of Fine Arts, Shenyang, 110000, China, China
2
Experimental Art Department, Luxun Academy of Fine Arts, Shenyang, 110000, China, China
3
College of Industrial Design,, Luxun Academy of Fine Arts, Shenyang, 110000, China, China
Submission date: 2024-02-03
Final revision date: 2024-04-21
Acceptance date: 2024-05-14
Publication date: 2025-06-16
Corresponding author
Guangpeng Yue
College of Industrial Design,, Luxun Academy of Fine Arts, Shenyang, 110000, China, China
College of Industrial Design,, Luxun Academy of Fine Arts, Shenyang, 110000, China, China
Archives of Civil Engineering 2025;71(2):99-112
KEYWORDS
high-resolution remote sensingdigital landscape architectureplanning and designforest stand structure
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
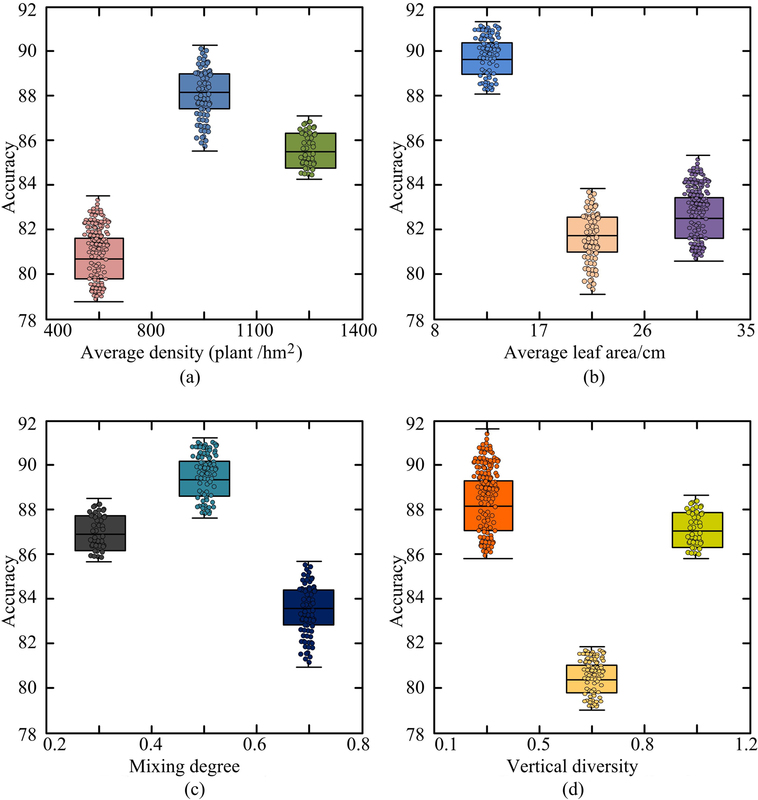
With the continuous development of remote sensing technology and the widespread application of high-resolution remote sensing images, digital landscape design based on high-resolution remote sensing image interpretation is gradually becoming a new design concept and method. This study is based on high-resolution remote sensing images to classify gardens, and combined with ground survey data, statistical analysis software is used to invert the landscape elements of gardens. The experimental results showed that the R2 value was relatively large, while the MRE and RMSE values were small, indicating that the analysis results were close to the true values and the fitting effect was relatively ideal. The overall image segmentation was excellent, with an average diameter at breast height of 8.0-17.0cm, mixing degree of 0.4-0.6, vertical diversity of 0.5-0.8, and a clear forest hierarchy when the average density was between 800-1100 plants/hm2. This indicates that the quality of landscape architecture designed at this landscape scale changes significantly and the effect is good. Digital landscape design based on high-resolution remote sensing image interpretation can not only improve design efficiency and accuracy, but also provide strong support for the sustainable development of urban planning and landscape design.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.