Analysis of the compactibility of bituminous mixtures for reflective crack relief interlayers (RCRI)
1
Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering, West Pomeranian University of Technology, Poland
Submission date: 2023-03-21
Final revision date: 2023-06-23
Acceptance date: 2023-07-11
Publication date: 2024-04-02
Corresponding author
Oliwia Merska
Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering, West Pomeranian University of Technology, Piastów, 70-310, Szczecin, Poland
Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering, West Pomeranian University of Technology, Piastów, 70-310, Szczecin, Poland
Archives of Civil Engineering 2024;70(1):201-217
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
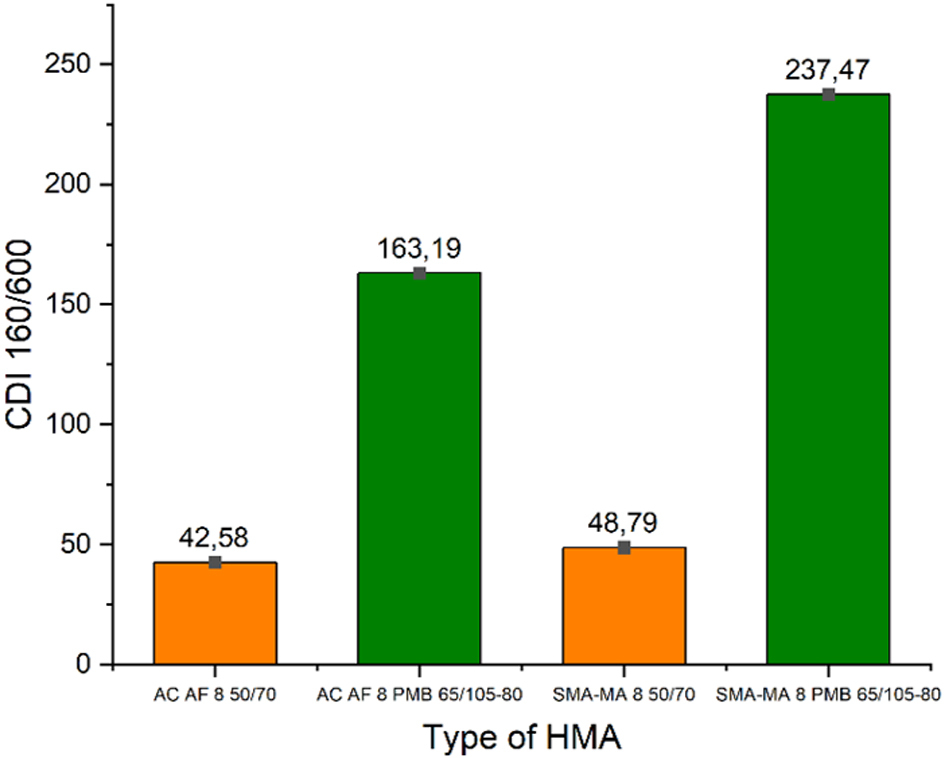
The physical properties determining the strength parameters of bituminous mixtures are strongly influenced by the processes of placement and compaction. This research focused on the assessment of compactibility of mixtures designed for reflective crack relief interlayers (RCRI) which, in most cases, are applied in thin layers. The materials analysed for compactibility in this research included AC – asphalt concrete, AC AF – asphalt concrete “anti-fatigue”,SMA - stone mastic asphalt and SMA-MA - stone mastic asphalt rich in bitumen mastic . The gyratory compactor method was used to determine the compaction slope K, the locking point LP and the compaction densification index CDI. The values of CDI show a substantially greater input of energy required for compaction of high-polymer modified mixtures, as compared to mixtures of the same design, yet containing the 50/70 bitumen. Locking point analysis showed that SMA and SMA-MA mixtures attain 98% relative compaction before reaching the locking point at which the aggregate skeleton starts to resist further compaction. This is quite the opposite as with the AC and AC AF mixtures. Among the tested mixtures the best compaction behaviour was observed in the case of SMA-MA 8 50/70, and this over a wide range of working temperature (100-160°C) and pressures (150kPa, 600kPa). The design of the mixture SMA-MA as an anti-fatigue layer assumes an increase in the content of filler and binder, as compared to conventional SMA. This composition provide a better compaction behaviour as compared to a conventional SMA mixture.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.