Analysis and field test of transverse force performance of assembled small box girder bridge
1
college of computer and control engineering, Northeastern Forestry University, China
2
college of mechanical and electrical engineering, Northeastern Forestry University, China
Submission date: 2024-07-09
Final revision date: 2024-08-23
Acceptance date: 2024-09-10
Publication date: 2025-12-01
Corresponding author
Archives of Civil Engineering 2025;71(4):465-480
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
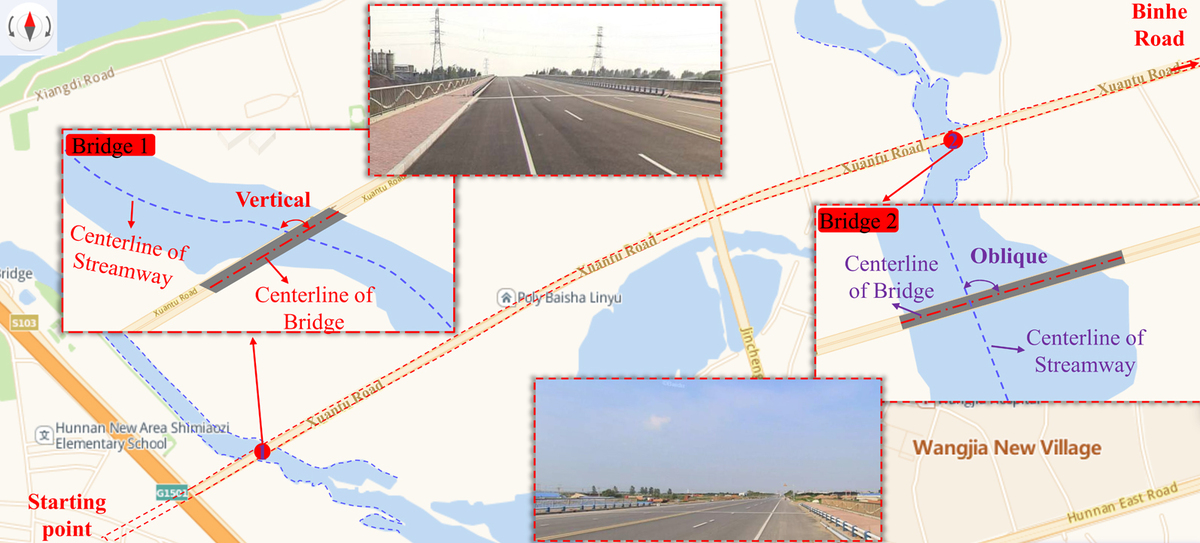
Continuous assembled box girder bridges are increasingly used in bridge engineering due to their high degree of assembly, short construction period, and high smoothness and comfort of traveling. To grasp the transverse force performance of this type of bridge structure, this paper, based on the industry standard drawings, adopts the method of finite element numerical analysis to systematically study the effects of different miter angles, number of diaphragm girders, span diameters, and width-to-span ratios on the transverse distribution coefficients of the loads and conducts the field test on the real bridge. The results show that the lateral distribution of main girder loads decreases with the increase of miter angle, the increase of the number of diaphragm beams, and the increase of span diameter, and increases with the increase of width-to-span ratio; the field static load tests were carried out on the three bridges, and the measured lateral distribution patterns of the bridge loads match well with the theoretical analysis of the finite element theory. The transverse distribution coefficients of the main girders obtained from the field test are reasonable, indicating that the force distribution of the transverse connection between the main girders is reasonable. The analysis of the transverse force of the assembled small box girder bridge can initially determine whether the bridge integrity is good or not, and provide technical data support for the subsequent operation and maintenance of the bridge.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.